Children’s Feet
Children’s feet are quite different from adults’ ones. Children’s bones are very soft in the early age, so they are more likely to be affected by abnormal forces and pressure. If a child can be assessed and diagnosed earlier, it will be easier to manage the condition. Below there are some of the most common conditions we treat at toe-tal podiatry. If you are concerned about a particular condition, please feel free to contact us.
Walking Abnormalities: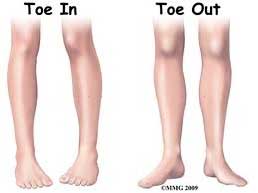
The walking abnormalities are the most common issues that presented in the clinic. The position of baby in uterus may result in some alignment issues, which may not resolve until children reach 3-4 years old. Some conditions which can be treated conservatively with great results are:
- Toe-walking (tip-toe)
- In-toeing (pigeon toed)
- Out-toeing
- Flat feet
- Limb length differences
Growing Pain:
Growing pain is defined as non-specific pains in the both leg, which normally occur at night or late afternoon. Children may complaint of leg pains, night cramps or sore legs after activity. It is often following rapid growth spurts. The reason of growing pain is still uncertain, but the main theories are fatigue, anatomical variation and overuse syndrome.
Delayed Development Difficulties
Children show some signs and symptoms of delayed developmental conditions. Some children may just slightly behind to reach their milestones; other may due to developmental or neurological disorders. Some common symptoms are tripping, clumsiness, reduced coordination, low muscle tone, and stiff gait patterns.
Sports Injuries:
We understand that children like to participate in sports, and active kids are more likely to get injured. The majority of sports injuries in children are found to involve the lower limb. Some of the bones in the lower limb are still growing till early adulthood. During this developing period, the children’s bones are vulnerable to injury and growth-related soreness. The common sports related conditions we encounter include:
- Osgood-Schlatter’ disease (knee pain)
- Sever’s disease (heel pain)
- Iselin’s disease (lateral foot pain)
- Freberg’s disease (forefoot pain)
Contact Us.
Please contact the appropriate location for bookings.
Salisbury Medical Centre
PH: 3277 1621 - Fax: 3277 2887
ACE Sports Medicine – Hibiscus Sports Complex
PH: 3349 5733 - Fax: 3349 5122
Acacia Ridge Day And Night Chemmart Pharmacy
PH: 3277 4220 - Fax: 3255 5644
Brisbane Medical Specialists – Tarragindi
PH: 3184 0400 - Fax: 3892 7094
Morningside General Practice Clinics – Morningside Plaza
PH: 3399 4685 - Fax: 3395 7377
Any other enquiries please email info@toetalpodiatry.com.au or call 0422 389 652
